 |
| Difference Between Analog And Digital Signal by Byjus |
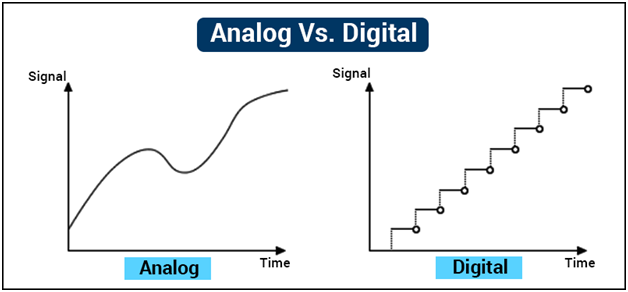
Have you ever seen a big, black record, or watched a movie at a drive-in movie theater where they use film rolls or maybe you remember learning how to read analog clocks? These are all examples of analog technologies. Analog technologies and recordings are when a device uses dials, arms or other measurements to create an analogy of the actual thing. If you measure a paperclip, the part of the ruler that is the same size as the paperclip of an analogy of the paperclip itself. On a clock with hands, the hands of the clock is an analogy of time passing. Then there is digital technologies. These are things like computers and cell phones. Instead of taking things and making analogies of them, digital technologies take the data and convert it into numbers that can be saved in the cloud. This is called sampling. Sampling is when you convert analog data into digital data and the other way around. Many people prefer digital recordings because they are easier and faster to use. They also take up less space. But their are some downsides. No matter how frequent sampling is, you will never get the whole story. This means that you will always be missing part of the picture. But this is something that many people sacrifice in order to continue to use digital technologies.
S&EP
SP3: Conducting Investigations
We looked at the differences between analog and digital recordings and found the pros and cons of each. We converted graphs using sampling and looked at different stories at different levels of sampling and through that found which technology we liked better. I personally still like digital data better than analog because though it leaves out part of the picture, you still have much easier access to it. No matter what level of sampling you use, you will still be missing pieces of information but I am willing to give this up for an easier and faster way to find things out.
XCC
XCC: Scale Proportion and quantity
Scale, proportion and quantity are very important when using analog and digital recordings. In analog technologies and recordings, the scale has to be perfect and the proportion can't be off. If it is, you can mess up the whole of the measurement. Take a watch for example. if you misjudge where the hand is pointing, you can get the time wrong. Quantity is also important when you are looking at sampling. Quantity is part of frequency and the frequency at which sampling is performed is important when trying to get almost an exact copy of the data you are trying to convert.
S&EP
SP3: Conducting Investigations
We looked at the differences between analog and digital recordings and found the pros and cons of each. We converted graphs using sampling and looked at different stories at different levels of sampling and through that found which technology we liked better. I personally still like digital data better than analog because though it leaves out part of the picture, you still have much easier access to it. No matter what level of sampling you use, you will still be missing pieces of information but I am willing to give this up for an easier and faster way to find things out.
XCC
XCC: Scale Proportion and quantity
Scale, proportion and quantity are very important when using analog and digital recordings. In analog technologies and recordings, the scale has to be perfect and the proportion can't be off. If it is, you can mess up the whole of the measurement. Take a watch for example. if you misjudge where the hand is pointing, you can get the time wrong. Quantity is also important when you are looking at sampling. Quantity is part of frequency and the frequency at which sampling is performed is important when trying to get almost an exact copy of the data you are trying to convert.



